Unveiling Melanoma: Understanding Subtle Symptoms and Hidden Dangers
Mar 13, 2024
Introduction:
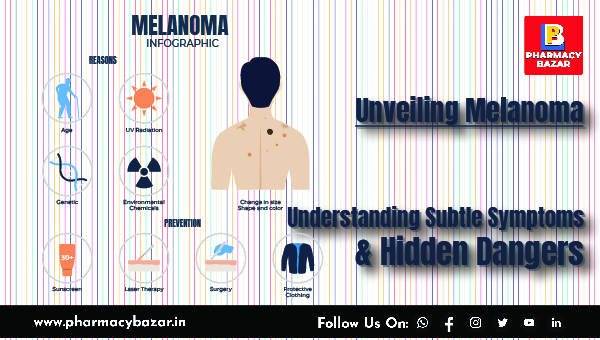
Melanoma, a formidable type of skin cancer originating in melanocytes, poses a significant health threat due to its potential to become fatal. Primarily developing on sun-exposed areas like the arms, face, and legs, melanoma also exhibits its insidious presence in less exposed regions, such as the spaces between toes, palms, soles, scalp, and genitals. This article explores the science behind melanoma, delving into its symptoms, hidden manifestations, and potential causes. Recognizing the subtle signs of this skin cancer is crucial for early detection, as timely intervention is key to effective treatment.
Understanding Melanoma Symptoms:
Melanoma often manifests subtly, making it imperative to pay attention to changes in the skin. The Cleveland Clinic emphasizes that nearly 30% of melanomas commence in existing moles, underscoring the importance of monitoring changes in the skin. Key symptoms to watch for include:
1. Asymmetrical Shape: Moles with irregular shapes, featuring markedly different halves.
2. Changes in Color: Growth with multiple colors or unusual color patterns.
3. Changes in Size: New growth in a mole larger than 1/4 inch (about 6 millimeters).
4. Changes in Symptoms: Alterations in symptoms, such as newfound itchiness or bleeding.
5. Unusual Border: Moles with atypical, notched, or scalloped borders.
It's essential to recognize that melanomas can vary in appearance, with some exhibiting all the mentioned changes, while others may only present one or two unusual characteristics.
Hidden Melanomas: Unveiling the Unseen Threats
Melanomas can emerge in unexpected areas with minimal sun exposure, challenging the conventional notion of its occurrence. These hidden melanomas include:
1. Melanoma inside the Body: Mucosal melanoma develops in mucous membrane tissues, affecting areas like the nose, mouth, esophagus, anus, urinary tract, and vagina.
2. Melanoma in the Eye: Ocular melanoma occurs beneath the white of the eye, impacting the uvea layer. Changes in vision can indicate eye melanoma, detectable during eye exams.
3. Melanoma under a Nail: Acral-lentiginous melanoma, a rare form, can manifest under fingernails or toenails and on the palms or soles.
Causes of Melanoma: Unraveling the Genetic and Environmental Factors
Despite ongoing research, the definitive cause of melanoma remains elusive. The intricate interplay between genetic and environmental factors likely contributes to the development of this skin cancer. While changes in DNA within skin cells play a role, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light emerges as a significant catalyst. UV light from the sun and tanning lamps can trigger melanoma, though it doesn't account for all cases, particularly those of hidden melanomas. Scientists are actively investigating other factors that may contribute to the onset of melanoma.
Melanoma can be influenced by various factors. Here are some of the key causes associated with melanoma:
1. UV Radiation Exposure:
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds is a major risk factor for melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, increasing the likelihood of cancerous mutations.
2. Age:
The risk of melanoma increases with age. While it can occur at any age, it is more commonly diagnosed in older individuals.
3. Genetics:
Family history of melanoma and certain genetic factors play a role in susceptibility to the disease. Individuals with a family history of melanoma are at a higher risk, and specific gene mutations, such as mutations in the CDKN2A and CDK4 genes, can contribute to an increased predisposition.
4. Skin Type and Color:
People with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes are more susceptible to the damaging effects of UV radiation and have a higher risk of developing melanoma compared to those with darker skin tones.
5. Moles and Atypical Moles (Dysplastic Nevi):
Having a large number of moles or atypical moles can increase the risk of melanoma. Atypical moles may exhibit irregular borders, uneven color, and larger size.
6. Immune Suppression:
Individuals with weakened immune systems, either due to medical conditions or immunosuppressive medications, are at an increased risk of developing melanoma.
7. Environmental Chemicals:
Exposure to certain environmental chemicals and toxins may contribute to the development of melanoma. However, the specific chemicals involved and their mechanisms are still areas of ongoing research.
8. Previous History of Skin Cancer:
Individuals who have previously been diagnosed with non-melanoma skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, are at an increased risk of developing melanoma.
9. Geographic Location:
Living in regions with high levels of UV radiation, such as sunny climates close to the equator, can elevate the risk of melanoma.
10. Hormonal Factors:
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or the use of hormonal therapies, may influence melanoma risk. Research is ongoing to understand the complexities of these relationships.
It's important to note that melanoma is often influenced by a combination of these factors, and individuals with multiple risk factors should take extra precautions, such as regular skin examinations and sun protection, to reduce their risk of developing melanoma. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can also aid in early detection and treatment.
Prevention:
Preventing melanoma involves a combination of protective measures and early detection. Here are several strategies for preventing melanoma:
1. Sunscreen and Sun Protection:
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) regularly, even on cloudy days. Apply it to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, ears, and hands.
-
Reapply sunscreen every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
-
Seek shade during peak sunlight hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) to minimize UV exposure.
2. Protective Clothing:
Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection, to shield the skin from direct sunlight.
3. Avoid Tanning Beds:
Avoid the use of tanning beds, as they emit harmful UV radiation that increases the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
4. Regular Skin Checks:
Perform regular self-examinations of your skin to monitor for any changes in moles, freckles, or the appearance of new growths. Report any suspicious changes to a healthcare professional.
5. Professional Skin Examinations:
Schedule regular skin examinations with a dermatologist, especially if you have risk factors for melanoma. Dermatologists can identify and monitor any suspicious lesions for early detection.
6. Early Detection Programs:
Participate in community-based early detection programs or screenings, especially if you have a family history of melanoma or other risk factors.
7. Educate Yourself:
Be aware of the signs and symptoms of melanoma, including changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of moles or skin lesions. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
8. Laser Therapy:
In some cases, laser therapy may be used to treat precancerous skin lesions or superficial melanomas. This involves the use of focused light energy to destroy abnormal skin cells.
9. Surgical Interventions:
Surgical removal is a common treatment for melanomas. Early-stage melanomas can often be completely excised, providing a cure. In advanced cases, more extensive surgery may be required, possibly including lymph node removal.
10. Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy:
Immunotherapy and targeted therapy are advanced treatment options for melanoma that can help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. These approaches may be considered in certain cases.
11. Counseling on Lifestyle Choices:
Encourage a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, which may contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of melanoma.
Remember that prevention and early detection are key in the management of melanoma. By adopting these preventive measures and staying vigilant about changes in your skin, you can minimize your risk and increase the chances of successful treatment if melanoma is detected. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Conclusion:
Melanoma, with its subtle symptoms and hidden manifestations, underscores the importance of vigilant skin monitoring. Early detection is pivotal for effective treatment, emphasizing the need for regular skin checks and awareness of potential signs. Unraveling the complexities of melanoma involves ongoing scientific exploration, shedding light on genetic and environmental factors. As we navigate the landscape of skin health, understanding the intricacies of melanoma becomes paramount in the quest for prevention and early intervention.
DISCLAIMER: This article is the property of Pharmacy Bazar and is protected by copyright laws. The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. The author and publisher of this article do not endorse any specific treatments, procedures, or products mentioned in this article.
Recent Post
Blood Cancer: Early Warning Signs and Diagnosis

Understanding Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Navigating Diabetes Medications: Benefits and Side Effects
Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment: How Unleashing T Cells' Energy Could Transform Immunotherapy

The Power of Lower Back Stretches: Benefits and Best Yoga Asanas for a Healthy Spine

8 Health Conditions That Could Be Due to Magnesium Deficiency

Unlocking Brain Health: How Lifestyle Choices Impact Cognitive Functions

When Speech Takes a Surprising Turn: Unraveling Foreign Accent Syndrome

The Optimal Time to Take Your Vitamin D Supplement: Insights and Best Practices

Beyond Diabetes: Unveiling the Hidden Health Risks of Insulin Resistance