UNDERSTANDING GALLBLADDER DISORDERS: SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT OPTIONS
Apr 29, 2023
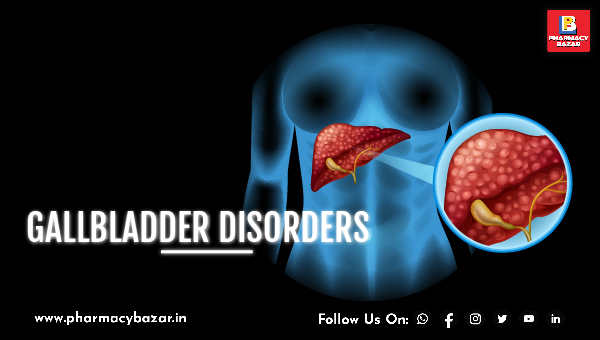
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located on the right side of the abdomen, just under the liver. Its primary function is to store and concentrate bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps to break down fats in the small intestine. When food containing fat enters the small intestine, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile into the small intestine through the bile ducts. This helps to emulsify and absorb the fat in the digestive tract. The gallbladder is not essential for life, but its removal can lead to changes in digestion and diet.
The symptoms of gallbladder disorder can vary depending on the specific condition, but some common symptoms include:
-
Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right quadrant
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Bloating and indigestion
-
Fever and chills
-
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
-
Clay-colored stools
-
Dark urine
-
Fatigue
-
Back pain, particularly between the shoulder blades
There are several diseases associated with the gallbladder, including:
-
Gallstones: These are the most common gallbladder disorders. They are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder and can cause pain and other symptoms.
-
Cholecystitis: This is inflammation of the gallbladder and can be caused by gallstones or an infection.
-
Biliary colic: This is a type of pain caused by gallstones that block the flow of bile from the gallbladder.
-
Choledocholithiasis: This is when a gallstone gets stuck in the bile duct and can cause pain, infection, and inflammation.
-
Gallbladder cancer: This is a rare but serious form of cancer that can develop in the gallbladder.
-
Gallbladder polyps: These are growths on the gallbladder wall that can sometimes be cancerous.
-
Gallbladder dyskinesia: This is a condition where the gallbladder does not contract properly, which can cause pain and other symptoms.
There are several diagnostic tests and procedures that can be used to diagnose gallbladder disorders. Some of the common ones are:
-
Ultrasound: This is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs. It can detect the presence of gallstones, inflammation, and other abnormalities.
-
Blood tests: Blood tests can help diagnose gallbladder disorders by measuring the levels of certain enzymes and other substances that are produced by the liver and gallbladder.
-
CT scan: A CT scan uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs. It can detect abnormalities such as gallstones, tumors, and inflammation.
-
HIDA scan: A HIDA scan is a nuclear medicine test that uses a special dye injected into a vein in your arm. The dye travels through your bloodstream to your liver and gallbladder, where it can be detected by a special camera. This test can help diagnose problems with bile flow and gallbladder function.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound: This is a minimally invasive procedure that combines an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end) and an ultrasound probe. It allows doctors to examine the gallbladder and surrounding organs in detail and can help detect abnormalities such as gallstones and tumors.
The treatment options for gallbladder disorder depend on the specific condition and the severity of the symptoms. Here are some common treatment options:
-
Medications: If the gallbladder disorder is caused by gallstones, medications such as ursodiol, chenodiol, and bile acid sequestrants may be prescribed to dissolve the stones.
-
Surgery: If the gallbladder disorder is severe and causes significant symptoms, surgical removal of the gallbladder may be recommended. This procedure is known as cholecystectomy and can be performed through traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery.
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This procedure involves using an endoscope to access the bile ducts and remove gallstones or other obstructions that may be causing the symptoms.
-
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL): This procedure uses shock waves to break up gallstones into smaller pieces, which can then be passed naturally out of the body.
-
Percutaneous cholecystostomy: This procedure involves the insertion of a tube through the skin and into the gallbladder to drain bile and relieve symptoms.
DISCLAIMER: This article is the property of Pharmacy Bazar and is protected by copyright laws. The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article. The author and publisher of this article do not endorse any specific treatments, procedures, or products mentioned in this article.
Recent Post
Blood Cancer: Early Warning Signs and Diagnosis

Understanding Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Navigating Diabetes Medications: Benefits and Side Effects
Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment: How Unleashing T Cells' Energy Could Transform Immunotherapy

The Power of Lower Back Stretches: Benefits and Best Yoga Asanas for a Healthy Spine

8 Health Conditions That Could Be Due to Magnesium Deficiency

Unlocking Brain Health: How Lifestyle Choices Impact Cognitive Functions

When Speech Takes a Surprising Turn: Unraveling Foreign Accent Syndrome

The Optimal Time to Take Your Vitamin D Supplement: Insights and Best Practices

Beyond Diabetes: Unveiling the Hidden Health Risks of Insulin Resistance